A new study highlights the powerful impact of diet on brain health, revealing that regularly consuming anti-inflammatory foods can reduce the risk of dementia by an impressive 31%.
This finding underscores the critical connection between what we eat and the health of our brain as we age. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats not only combat inflammation but also support cognitive function by promoting better blood flow, reducing oxidative stress, and nourishing brain cells.
The study, published Monday in the journal JAMA Network Open, stated that this was evident even in individuals already diagnosed with cardiometabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, or stroke.
Read on to learn more about the link between brain health and your diet!


How Anti-Inflammatory Foods Can Reduce Dementia Risk By 31%
Abigail Dove, lead author of the study and a doctoral student at the Aging Research Center at Karolinska Institutet in Solna, Sweden, said, "Following an anti-inflammatory diet was related to a lower risk of dementia, even among people with cardiometabolic diseases who are already at elevated risk of dementia."
Interestingly, those with type 2 diabetes, stroke, or heart disease who consumed an anti-inflammatory diet “developed dementia 2 years later than those with cardiometabolic diseases and a pro-inflammatory diet,” she noted.
Although the study is observational and cannot establish cause and effect, brain scans of participants who followed an anti-inflammatory diet revealed significantly lower levels of biomarkers associated with neurodegeneration and vascular injury.
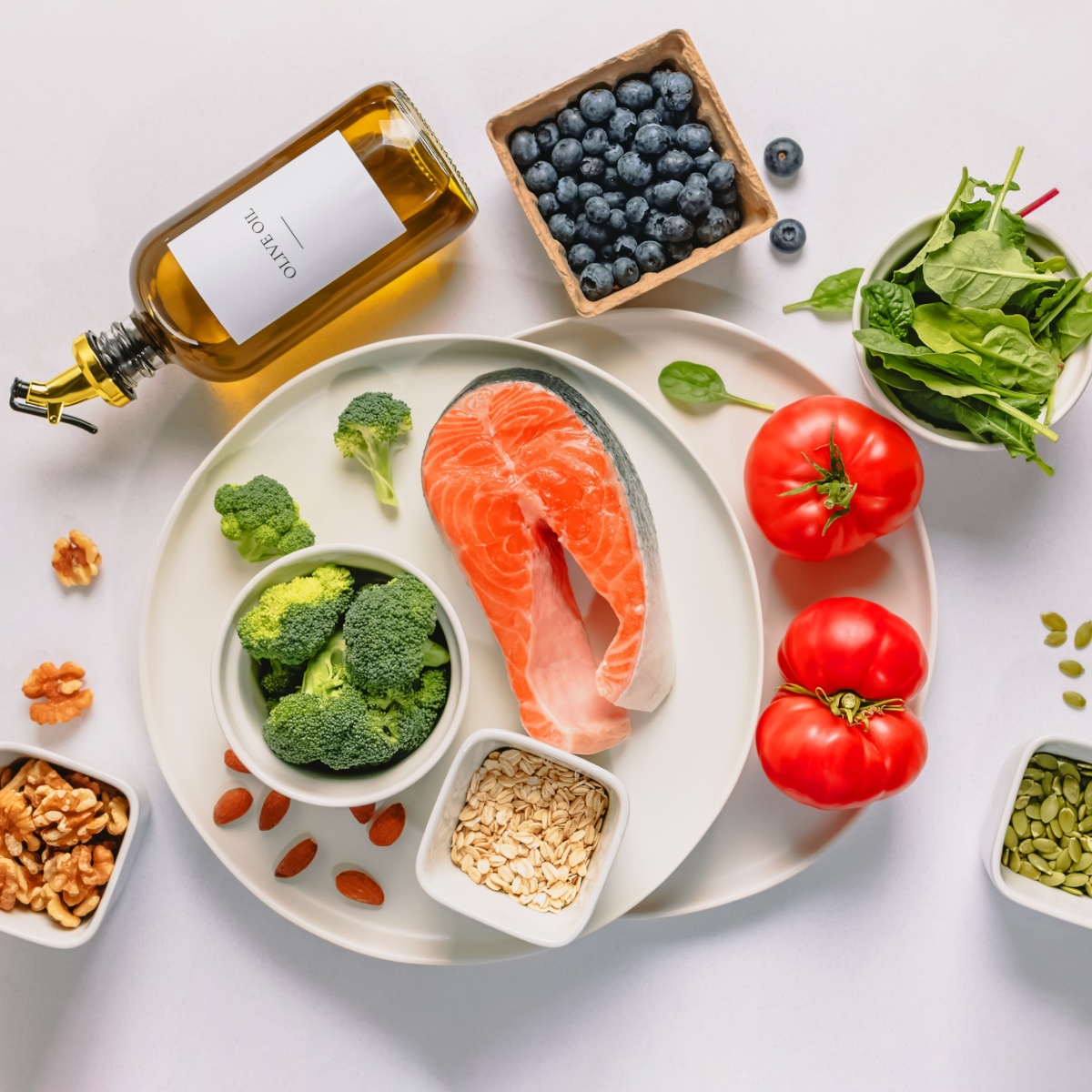

Inflammatory Diet Versus Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An inflammatory diet typically includes foods that promote inflammation in the body, such as processed meats, refined carbohydrates, sugary snacks, and foods high in unhealthy fats like trans fats and saturated fats. These foods can trigger or exacerbate chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions.
In contrast, an anti-inflammatory diet emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods that help reduce inflammation. This includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats like those found in olive oil and fatty fish. These foods are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients that support overall health and combat inflammation at the cellular level.
In addition to dietary choices, certain lifestyle habits can also contribute to chronic inflammation. Sedentary behavior, chronic stress, poor sleep quality, and smoking are all inflammatory lifestyle factors that can compound the effects of an unhealthy diet.
On the other hand, regular physical activity, stress management techniques, adequate sleep, and avoiding tobacco use are key components of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
Together, these dietary and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce inflammation, supporting better health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and boosting your brain health!