Spices are more than just flavor enhancers—they are packed with powerful compounds that offer a range of health benefits. Many spices have anti-inflammatory, metabolism-boosting, and cancer-fighting properties, making them a great addition to a healthy diet.
We checked in with several health experts to discover four anti-inflammatory spices that can aid in weight loss and even cancer risk prevention. According to them, turmeric, black pepper, cinnamon, and ginger are the ones to include in your diet. Read on to learn more.
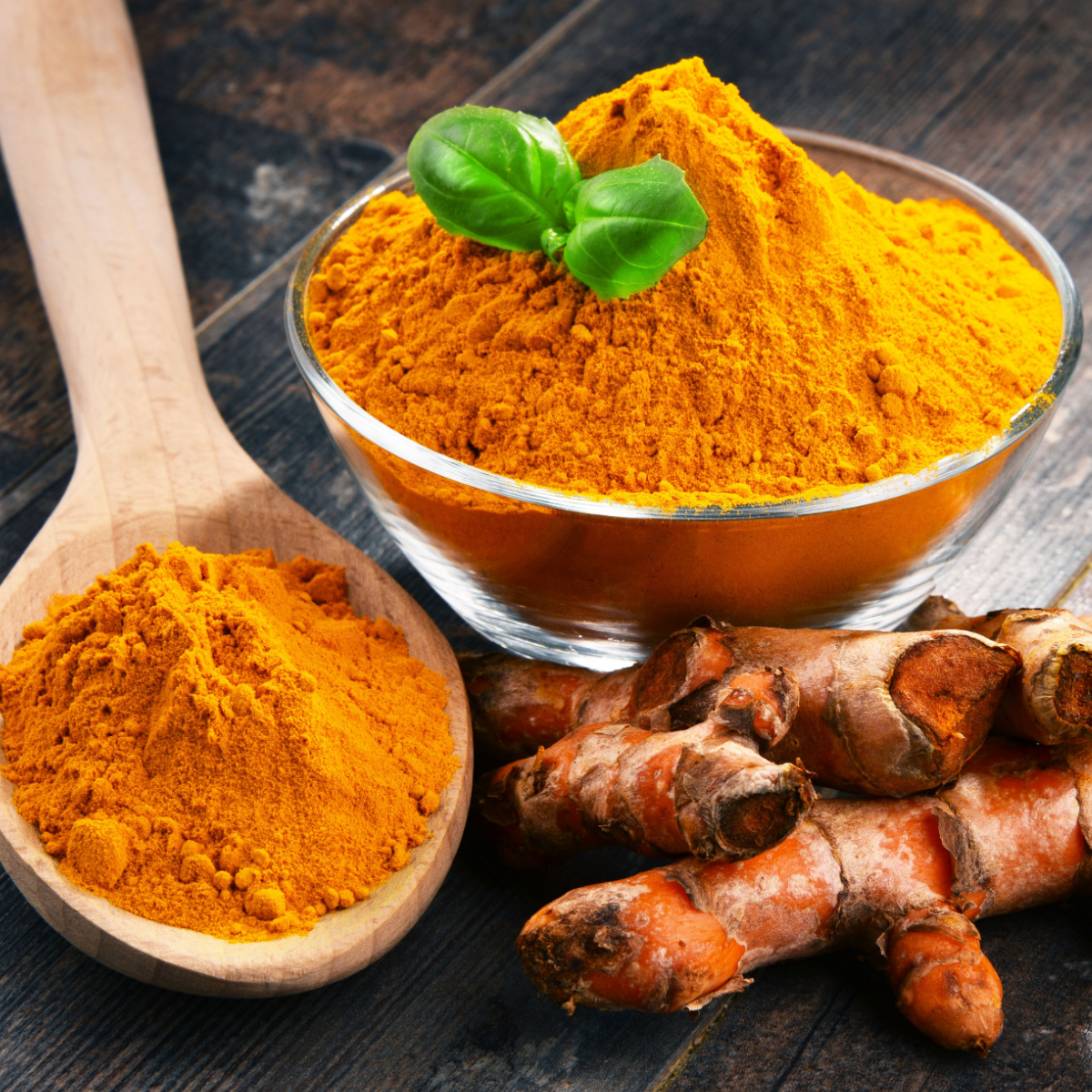


1. Turmeric
Turmeric, a vibrant yellow spice, has gained significant attention for its potential health benefits, particularly in reducing chronic inflammation. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Additionally, curcumin has been studied for its role in supporting weight loss and reducing belly fat.
Curcumin has also been studied for its potential to fight cancer-causing properties and anti-cancer effects.
"Turmeric contains an active compound called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. By reducing inflammation, it may support weight loss, including belly fat. Curcumin can also potentially aid in improving insulin sensitivity, influencing how the body stores fat," Kimberly Booker, RD, says. As for its role in chronic inflammation, she notes that "curcumin in turmeric acts as a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that contribute to inflammation. By reducing oxidative stress, turmeric helps manage chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues."
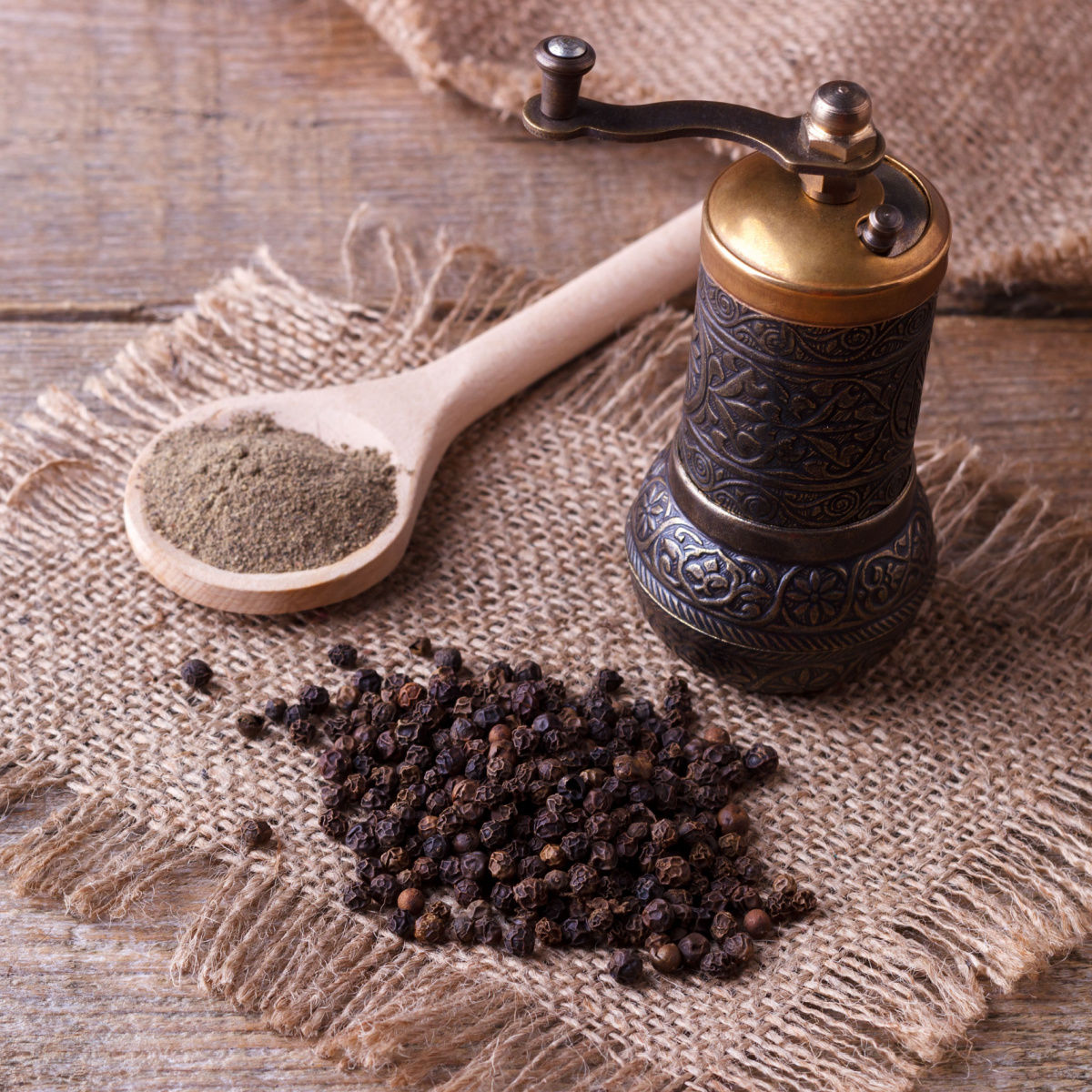

2. Black Pepper
Black pepper, derived from the Piper nigrum plant, is not only a common kitchen staple but also a spice that may contribute to reducing chronic inflammation and potentially aid in minimizing abdominal fat.
Booker elaborates further and says, "Piperine, the active compound in black pepper, has been linked to potential improvements in fat metabolism. It may enhance the absorption of other nutrients, including those that support weight loss."
Piperine has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which can help reduce the oxidative stress and inflammation associated with cancer development.
As far as its connection to minimizing chronic inflammation, Booker highlights that "piperine exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to a reduction in chronic inflammation. Pairing black pepper with other spices can enhance their bioavailability and effectiveness."
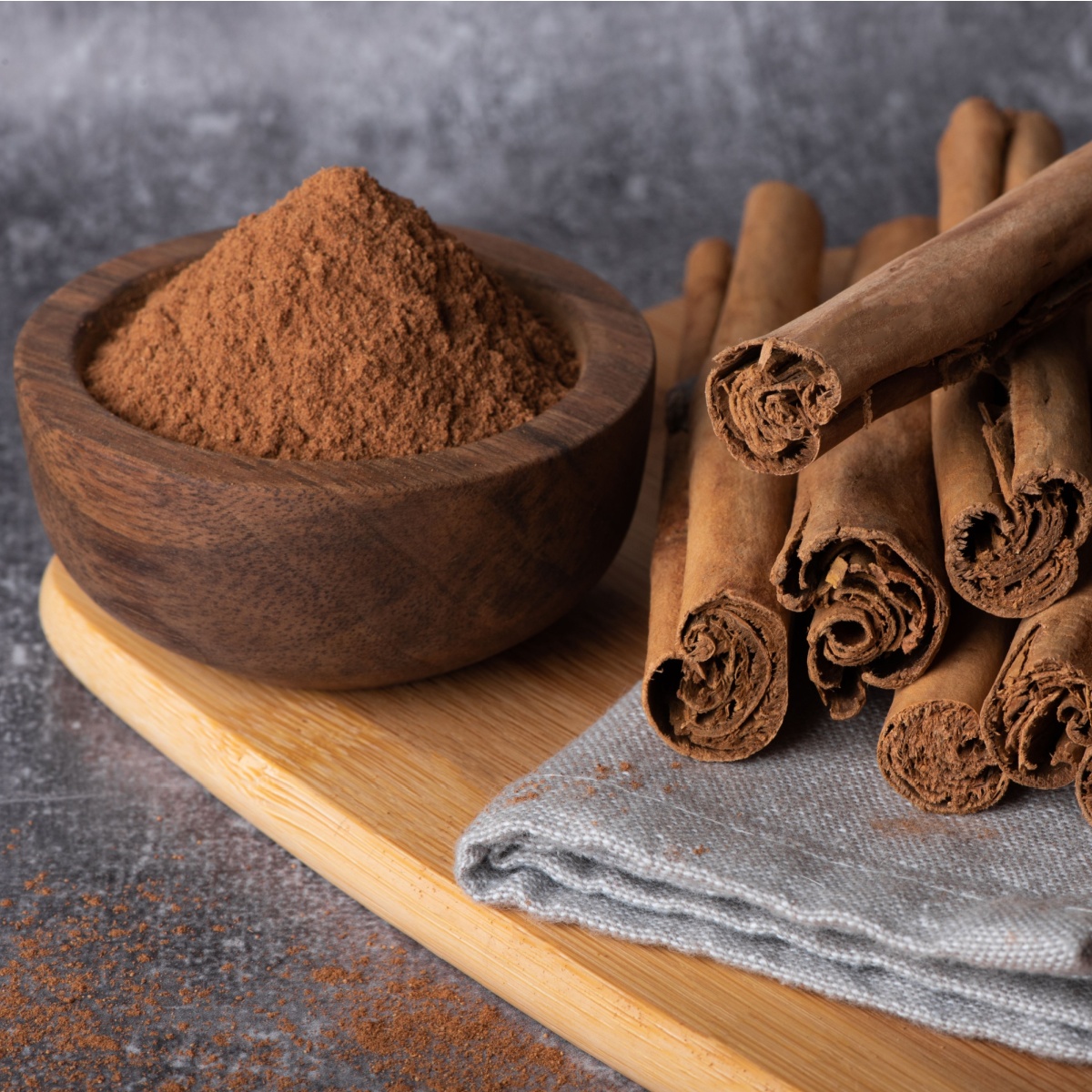

3. Cinnamon
Cinnamon, a beloved spice known for its warm and comforting flavor, offers more than just a delightful taste. Rich in antioxidants and possessing potent anti-inflammatory properties, cinnamon can help soothe digestive discomfort and reduce bloating by calming inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, cinnamon has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels, which can aid in weight loss by promoting better glucose control and reducing cravings for sugary foods.
"One of the best anti-inflammatory spices is cinnamon," says dietitian Trista Best, adding that this spice "contains powerful antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the body."
Nutritionist Mary Sabat agrees and says, "Cinnamon contains anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce bloating by aiding in digestion," she tells us. These advantages arise from an antioxidant compound found in the spice known as cinnamaldehyde.
Cinnamaldehyde, in particular, has been found to inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells and may prevent their spread by affecting various molecular pathways involved in cell growth and survival.
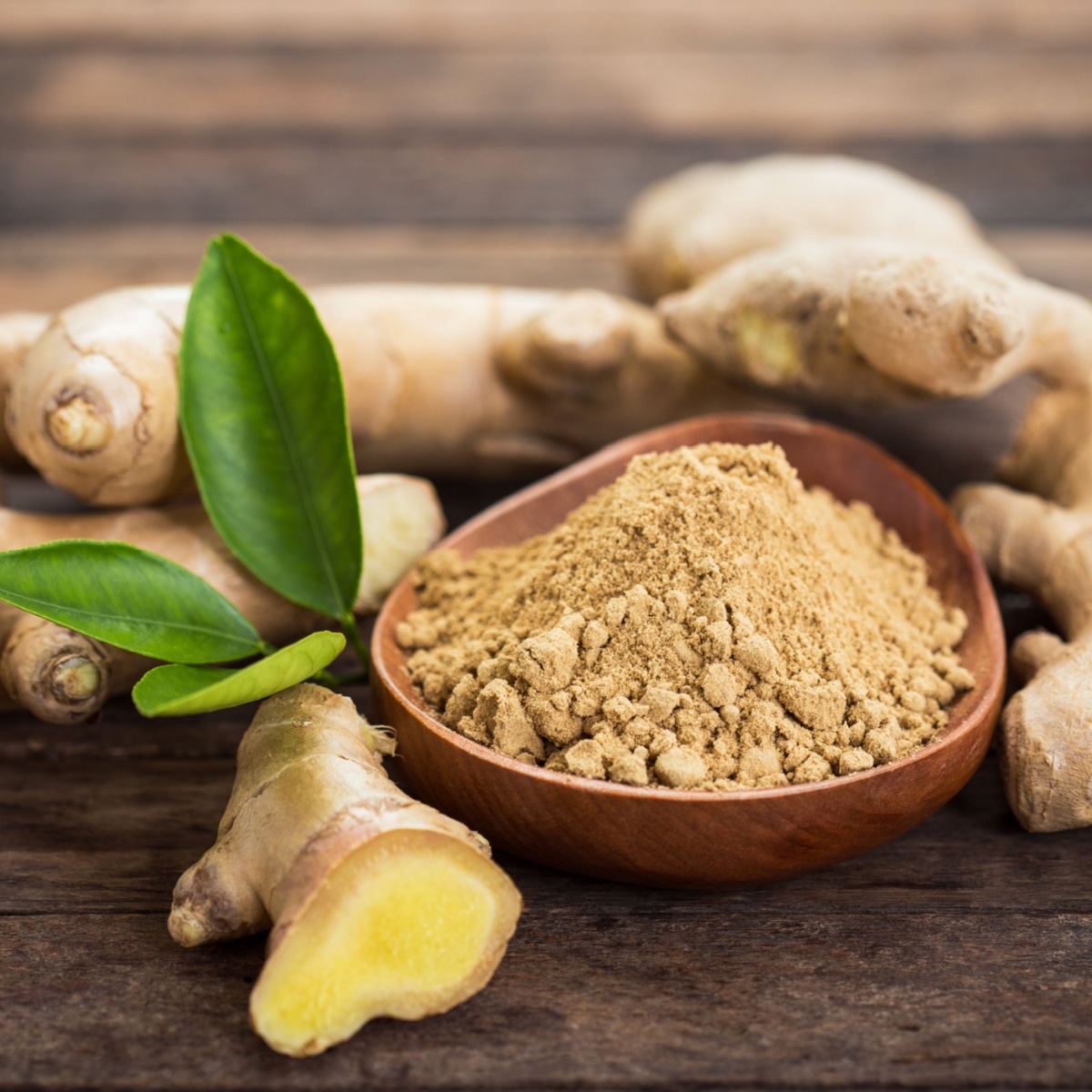

4. Ginger
Another spice to add to the list is ginger! Both Best and Dr. Melina Jampolis agree that ginger is a smart addition to cooking, known for its ability to alleviate inflammation, bloating, and gas.
"Ginger is unique to weight loss in that it contains compounds known as gingerols and shogaols," Best tells us. "These compounds create an antioxidant effect in the body that reduces free radical damage in the body. This damage leads to an increase in oxidative stress that can both cause and exacerbate obesity (both of which are linked to cancer development). This damage occurs at a cellular level, and once those damaged cells replicate, the body's natural processes that maintain homeostasis can become disrupted, leading to decreased metabolism, energy, and more."
"Ginger reduced the body mass index (BMI) of obese women in one study after they ate two grams (approximately 1/2 teaspoon) of ginger powder per day," Dr. Jampolis adds. "It slightly increases the number of calories we burn, helps with satiety (fullness) as it reduces the amount of food we eat, and improves the health of the gut microbiome."