Carb-loaded foods, rich in sugars and refined carbohydrates, have a profound impact on various aspects of health. These foods, often processed and lacking essential nutrients, can contribute to adverse effects on blood sugar levels, metabolism, and insulin resistance. When consumed in excess, high-carb foods can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar, followed by crashes, putting stress on the body’s ability to regulate glucose.
We spoke with Michelle Saari, MSc, RD from eHealth project; and Lisa Richards, creator of The Candida Diet, to learn about the five carb-loaded foods that can spike your blood sugar, slow your metabolism, and lead to insulin resistance. They revealed that breakfast cereals, canned fruit in syrup, baked goods, granola bars, and sweetened beverages are the culprits to watch out for.
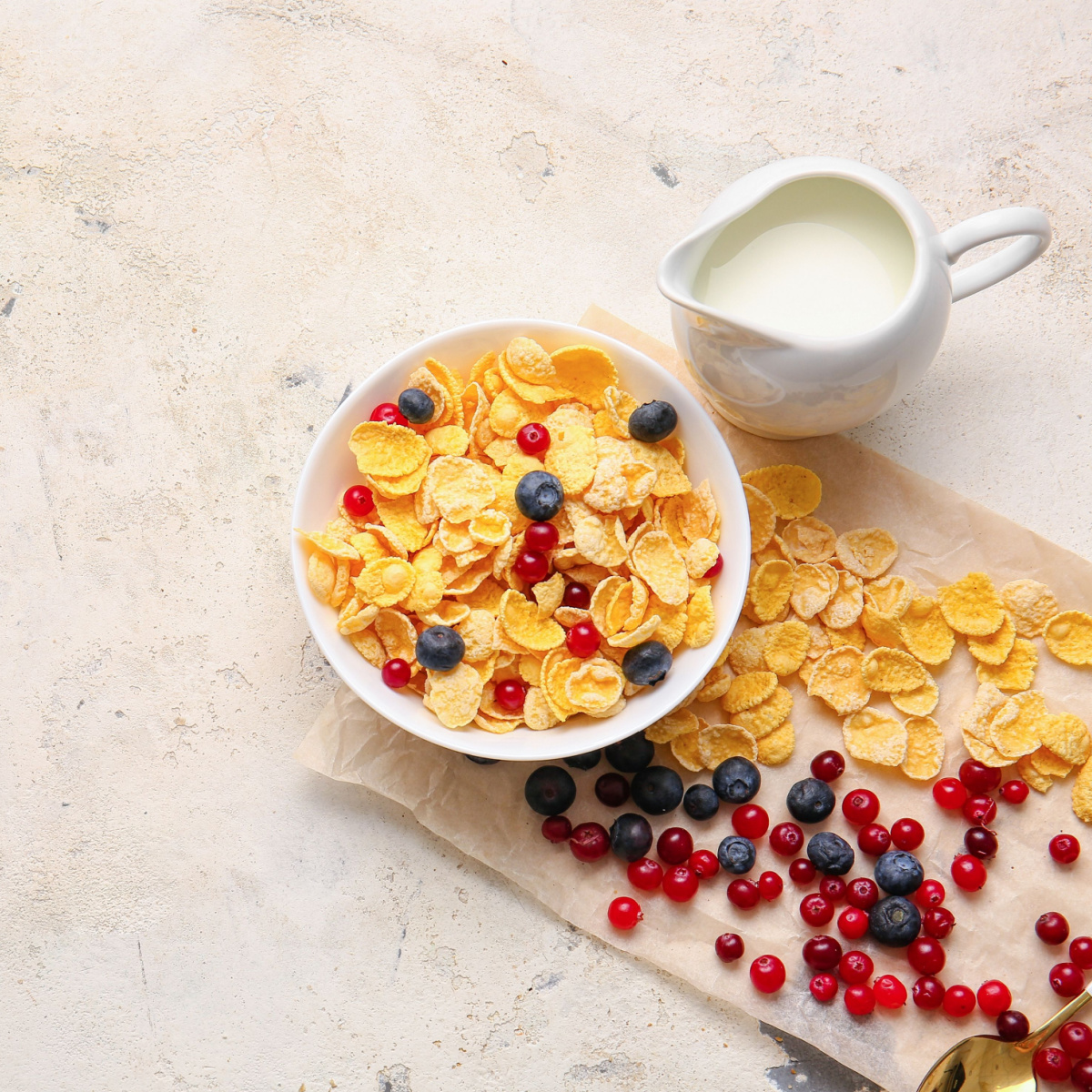


Breakfast Cereal
Breakfast cereals, often perceived as a convenient morning option, can have significant implications for health. Many commercially available cereals are laden with refined sugars and processed carbohydrates, contributing to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels when consumed. This spike is typically followed by a subsequent crash, leading to fluctuations in energy levels and potential cravings for more high-carb foods. The repetitive consumption of such cereals may also contribute to a slowing of metabolism over time, making weight management more challenging. Moreover, the persistent exposure to high levels of refined carbs can contribute to insulin resistance.
"Not all breakfast cereals are made equal, but they tend to be high in sugar without much other nutritional value. If a cereal doesn’t have fiber, then there is nothing to help regulate your blood sugars. If you want to have a morning breakfast cereal, look for one that has less than 10% of the calories from sugar, ideally there should be no sugar added to it at all. You can help to regulate your blood sugars by eating it with chopped fruit for a source of fiber, and milk which is a good source of protein. By having protein and fiber with foods it can help to slowly release sugar to your blood steam which helps to control blood sugar spikes," Saari says.
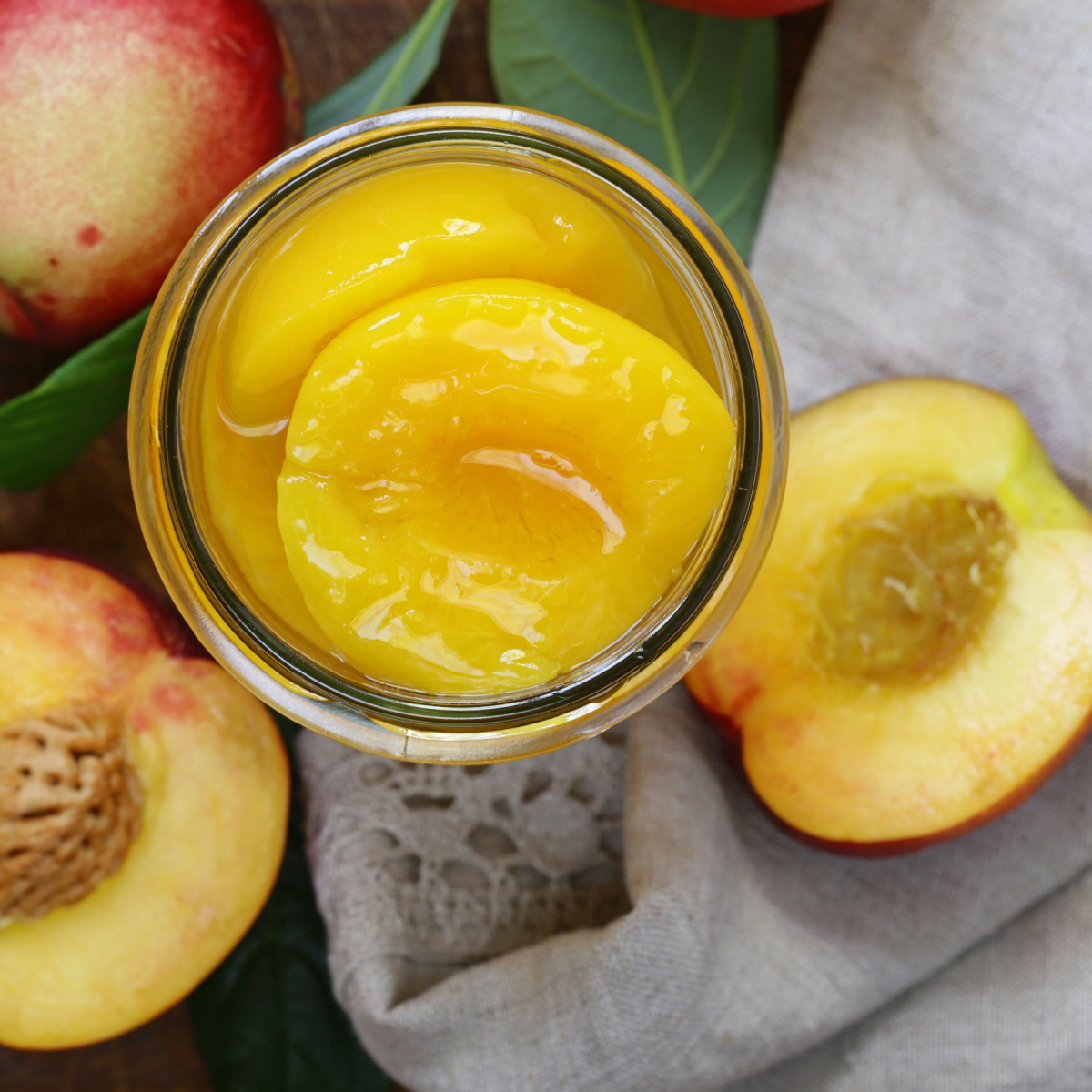

Canned Fruit in Syrup
Canned fruits in syrup may seem like a convenient and tasty option, but they often come with a downside for your health. The syrup in which these fruits are preserved is typically loaded with added sugars, which can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels upon consumption. The frequent consumption of such sugary syrups can contribute to energy fluctuations and cravings. Moreover, the excess sugar intake can over time lead to a slowing of metabolism, making it more challenging to manage weight effectively.
"Canned fruit that is preserved in syrup is not equivalent to fruit by itself. The syrup is typically high in added sugar in order to preserve it. I don’t recommend having fruit cups at all, but if you do, there are some that are preserved in water which can reduce the added sugars. If your only option is fruit cups preserved in syrup, before you eat it, put it through a strainer and rinse it with water. This can help to wash off most of the syrup that was on the fruit."
Additionally, a diet consistently high in added sugars, as found in canned fruit syrups, may contribute to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of metabolic issues.
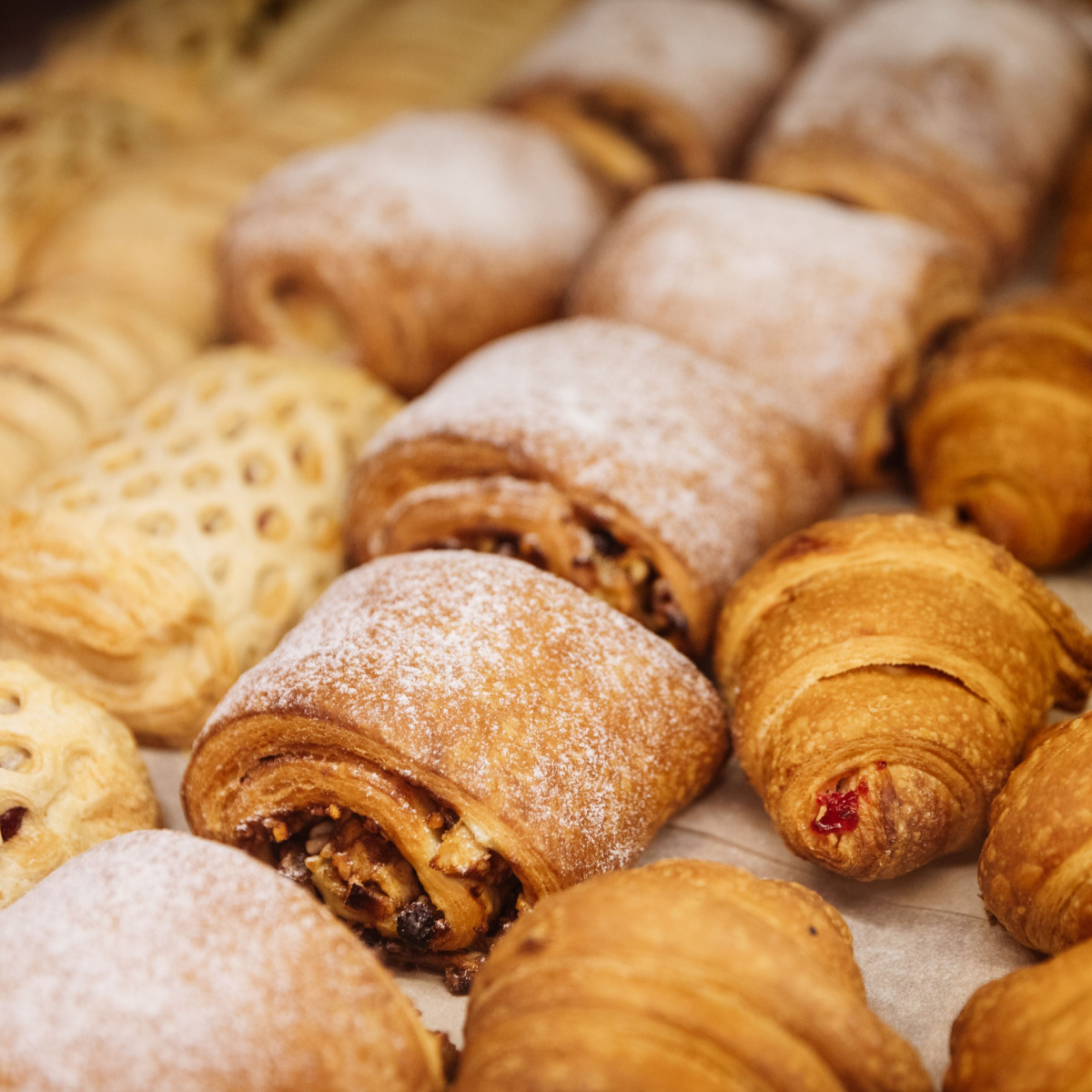

Baked Goods
Baked goods, often tempting with their delicious aromas and textures, can have repercussions on blood sugar, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Many baked goods, such as pastries and cookies, are frequently laden with refined sugars and processed carbohydrates. The rapid digestion of these sugars can lead to a quick spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a subsequent crash, resulting in energy fluctuations and potential cravings for more sugary foods. Additionally, the persistent consumption of such refined carbs may contribute to a slowing of metabolism, making weight management more challenging.
Saari shares her alternatives to baked goods which won't cause your blood sugar to spike, slow your metabolism, or cause insulin resistance. "[Baked goods] are loaded with fat and sugar, none of which are beneficial for your health. Rather than stopping at the coffee shop for a pastry, make sure that you have something prepared for yourself in the morning to grab on the go. Making some toast and putting all natural peanut butter and bananas on it. These are both better options than buying baked goods."
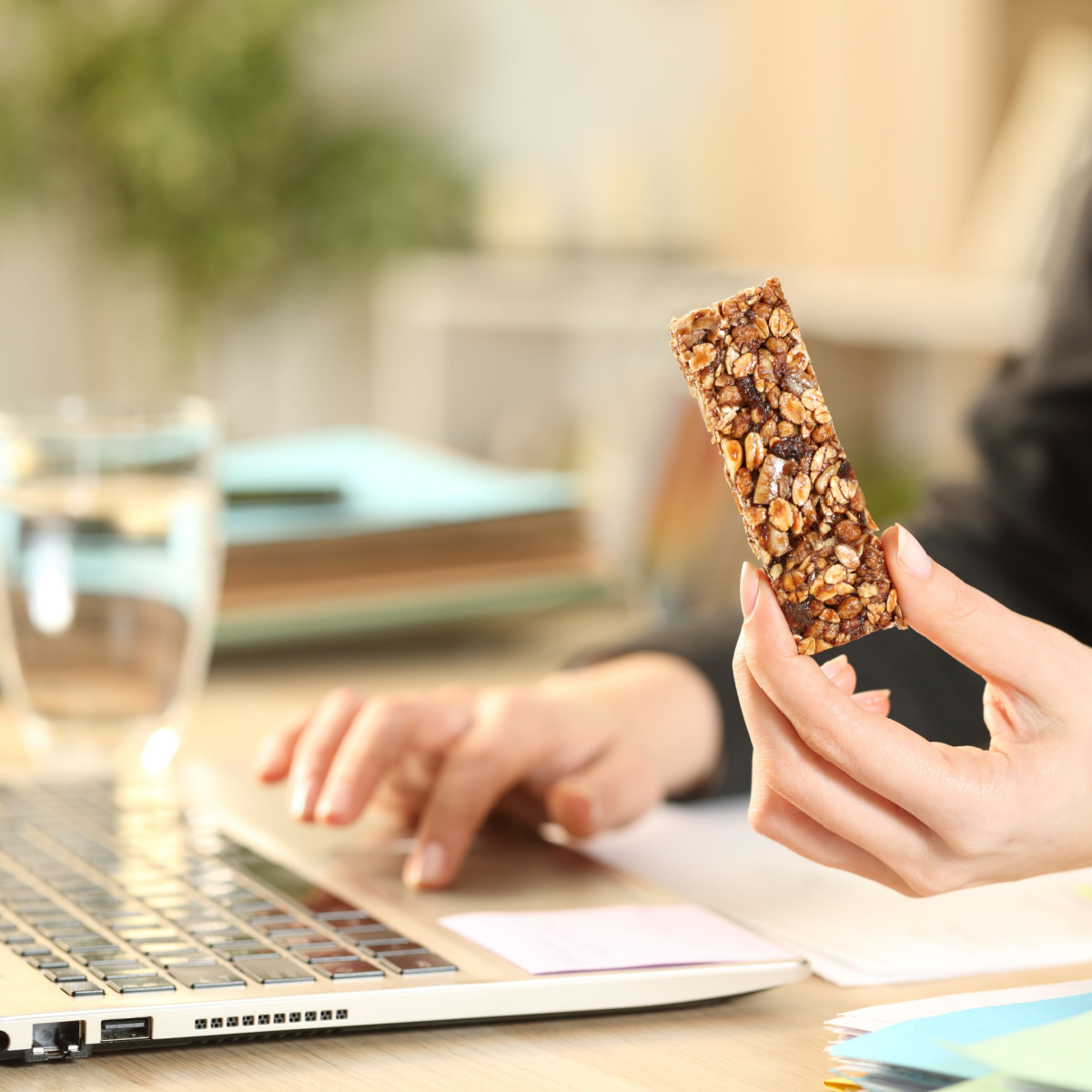

Granola Bars
Granola bars, often perceived as a quick and wholesome snack, can have implications for blood sugar, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Many commercially available granola bars contain significant amounts of added sugars and processed carbohydrates, contributing to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels upon consumption. This sudden surge is usually followed by a crash, which then lead to fluctuations in energy levels and possible cravings for more foods that are high in carbs. Moreover, the consistent intake of these sugary and high-carb snacks may contribute to a slowing of metabolism. Additionally, the persistent exposure to high levels of added sugars can contribute to insulin resistance.
"These are glorified chocolate bars without the satisfaction that you get from eating a chocolate bar. They are high in added sugar and high in calories for a very small amount. Skip the granola bars because they really aren’t adding anything to your diet. If you need a snack throughout the day try making your own trail mix with mixed nuts for protein and healthy fat, popcorn for fiber and whole grains, and a piece of fruit for fiber. This is the ultimate combination to help manage blood sugars and reduce the risk of insulin resistance," says Saari.

Sweetened Beverages
Sweetened beverages, including sodas, fruit drinks, and sweetened teas, pose a significant threat to blood sugar regulation, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Packed with high levels of added sugars, these drinks can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels upon consumption. The ensuing crash can lead to energy fluctuations and increased cravings for more sweetened beverages that are laden with sugar. Regular intake of sweetened beverages has also been linked to a slowing of metabolism. Additionally, these high-sugar drinks may contribute to insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, increasing the risk of metabolic issues and type 2 diabetes.
The high sugar content of these beverages "can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to inflammation in the body. Sugary drinks have been associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems," Richards notes.