High-calorie foods are vital for providing the energy needed for optimal bodily function, with metabolism playing a key role in converting these nutrients into usable energy. However, the intricate relationship between high-calorie foods and metabolism involves a delicate balance. While essential for sustaining energy levels, excessive consumption, particularly of processed and sugary foods, can negatively impact metabolism.
To learn about which high-calorie foods we should stay away from because of their negative effects on metabolism, we spoke with Dr. Velusamy of iCliniq, and Catherine Gervacio, registered nutritionist-dietitian & certified exercise nutrition coach. They revealed that sugary beverages, fried foods, processed snacks, and highly processed sweets are the ones to avoid.
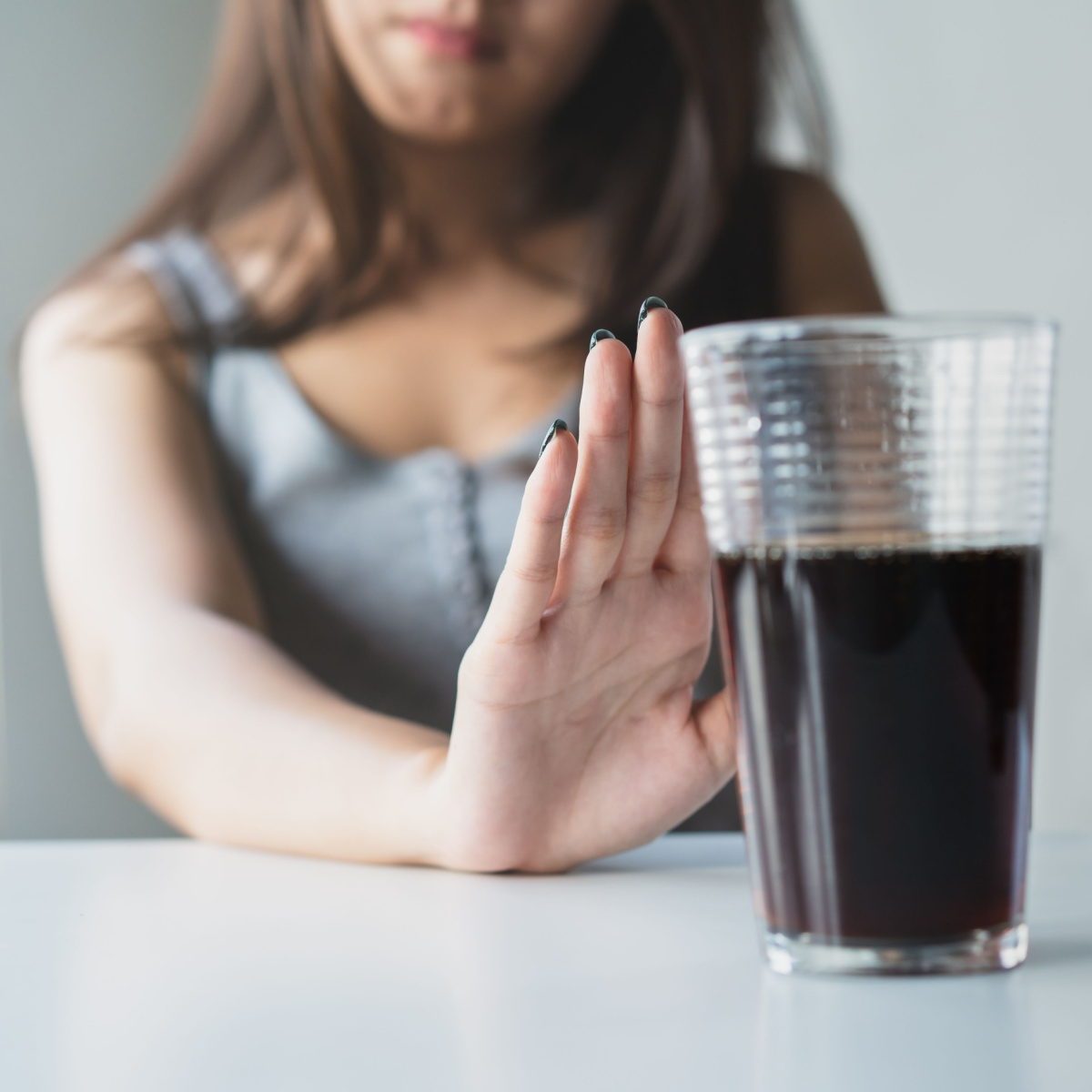


Sugary Beverages
Sugary beverages, characterized by their high-calorie content primarily from added sugars, pose a significant threat to metabolic health. Consuming excessive amounts of sugary drinks has been linked to an increased risk of insulin resistance, weight gain, and metabolic syndrome.
Dr. Velusamy says, "Energy drinks and sodas are well known for having a lot of sugar. These calories are empty and can cause metabolic disruption and weight gain. Drinking sugary beverages causes a sudden spike in blood sugar level. In order to control the excess sugar the pancreas will secrete insulin. Insulin resistance, a disorder in which cells lose their sensitivity to insulin, can develop over time as a result of frequent exposure to high sugar loads. Consequently, the body's capacity to control blood sugar levels and metabolism will be compromised."
Gervacio further elaborates on soda specifically and adds: "[Soda] can increase fat accumulation in the body, affecting metabolism. This happens when the body converts excess sugar, particularly fructose which is present in regular sodas, into fat in the liver. This process can lead to the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area, contributing to metabolic issues and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease."
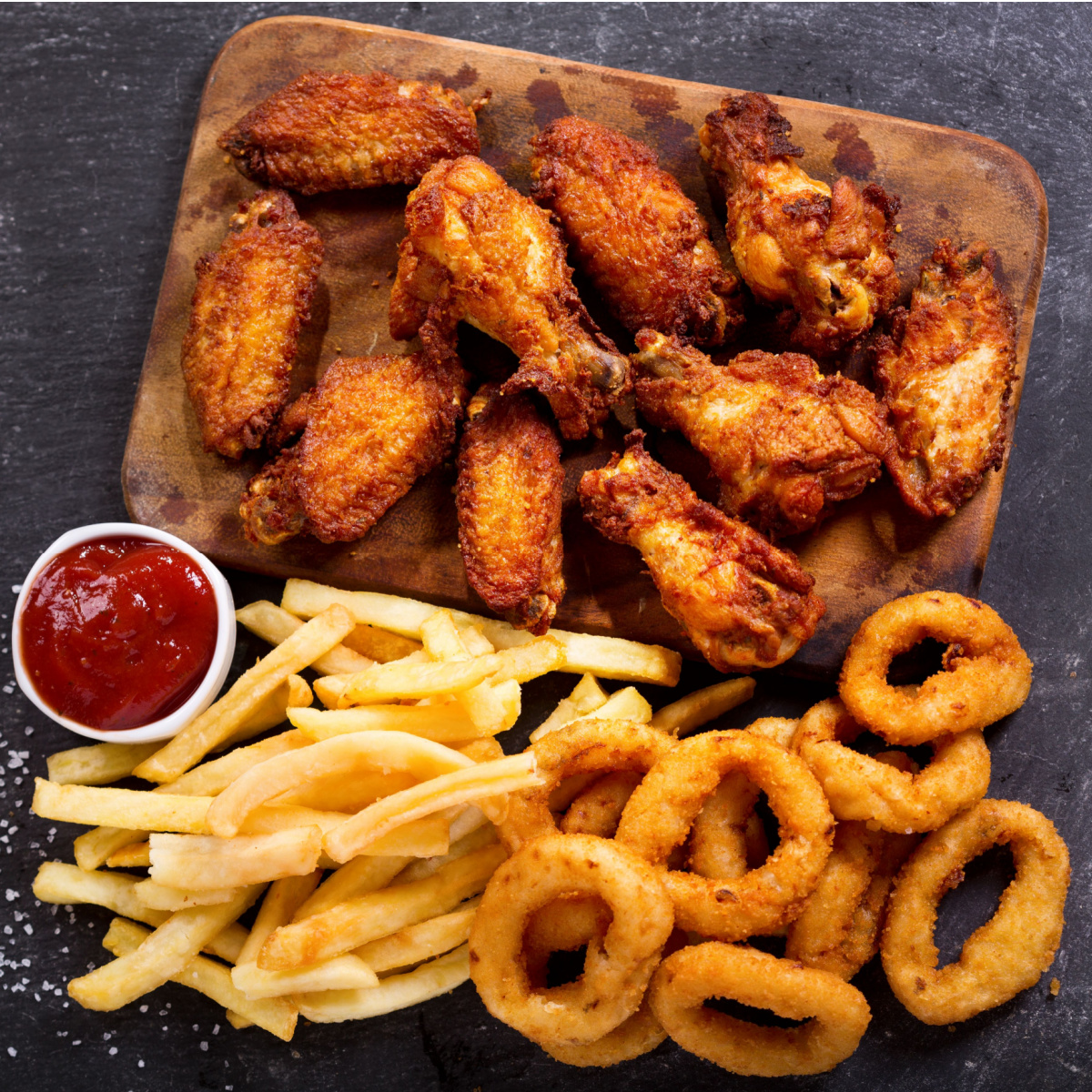

Fried Foods
Fried foods, often high in unhealthy trans fats and laden with excess calories, can have detrimental effects on metabolism when consumed excessively. The cooking process involving deep frying at high temperatures can introduce harmful compounds, and the resulting trans fats may contribute to inflammation and insulin resistance.
"While frying treats may please your palate, consuming too many calories from them might slow down your metabolism and make it more difficult for your body to burn calories. Fried foods are frequently high in saturated and trans fats, which are bad for your health. Increases in LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, or "bad" cholesterol, can result from a diet heavy in these fats. Increased inflammatory response and insulin resistance are two conditions that can have a detrimental effect on metabolism and are both facilitated by elevated LDL cholesterol levels," Dr. Velusamy says.
Gervacio cites french fries as one example from a comprehensive list, providing detailed explanations of their adverse effects. "They are deep-fried in unhealthy oils which may elevate bad cholesterol (LDL). The oils used are commonly high in trans fats and saturated fats which can lead to elevated cholesterol levels and insulin resistance. Also, the process of deep-frying potatoes may generate harmful compounds and free radicals, which promote inflammation. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the metabolic processes in the body."
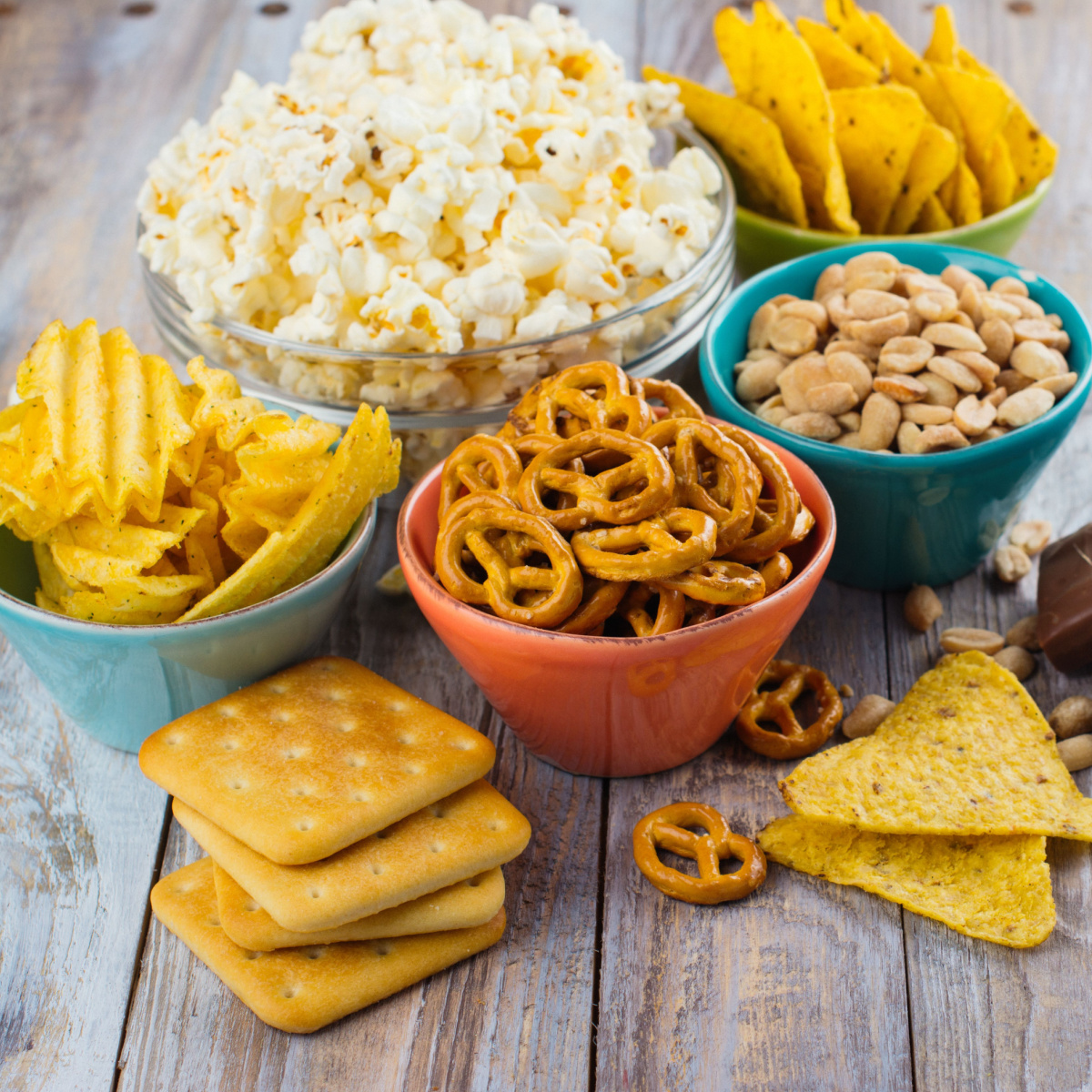

Processed Snacks
These convenient but nutritionally poor snacks contribute to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction. The high levels of added sugars and refined carbohydrates in processed snacks can lead to insulin resistance, disrupting the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Dr. Velusamy highlights that "a lot of processed snacks are high in trans fats, refined sugars, and empty calories, which can cause long-term harm in addition to causing weight gain and metabolism disruption. High concentrations of harmful fats, additives, and refined sugars can be found in many processed foods. Both metabolic dysfunction and weight gain may be exacerbated by these components. Furthermore, processed snacks frequently lack important nutrients, which encourages overindulgence in empty calories that do not supply the energy needed for good metabolic performance."
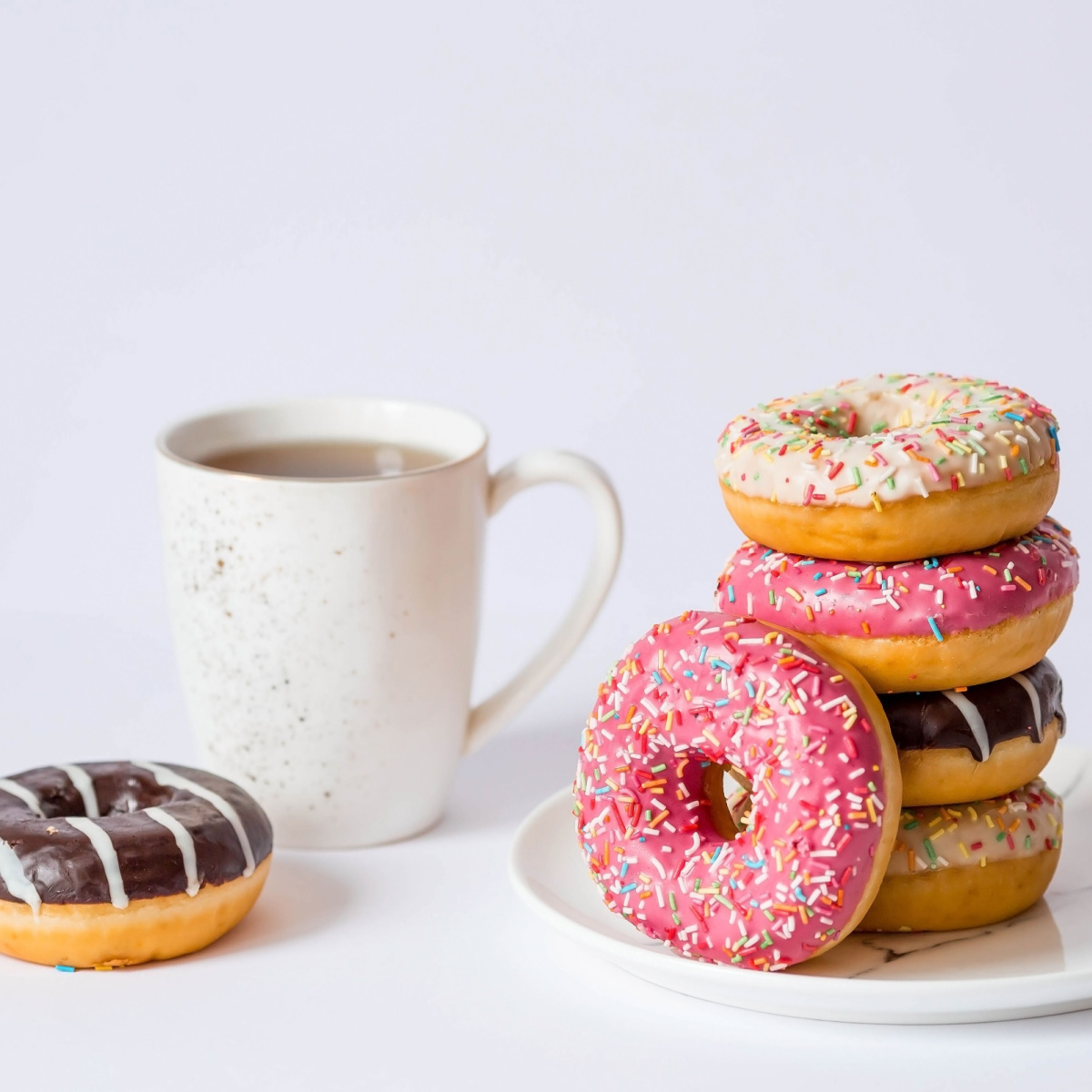

Highly Processed Sweets
Despite being highly addictive, processed sweets provide minimal nutritional value and can contribute to metabolic issues with excessive consumption. While the occasional indulgence in a sweet treat may not pose a significant threat, it is crucial to be mindful of its impact on health, as these treats can become addictive when cravings arise.
"Desserts heavy in fat and sugar can upset your body's metabolic balance, causing weight gain and impairing your body's capacity to burn calories. Desserts high in sugar and bad fats can aggravate inflammation and insulin resistance. Excessive consumption of refined sweets can cause blood sugar fluctuations, which strain the body's insulin-producing systems. This can eventually make it more difficult for the body to properly absorb and use calories, which will have a detrimental effect on metabolism," says Dr. Velusamy.
Gervacio highlights donuts as one example of how processed sweet treats can hurt your metabolism, "They are loaded with added sugars and trans fat which can contribute to insulin resistance and weight gain. High intake of sugar causes the cells to become less responsive to insulin. As a result, it impairs the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, which then affects metabolism. This harms the body by putting it at risk of type 2 diabetes and weight gain, too."